Overclocking is the process of making your processor (CPU or central processing unit) run faster. The performance is already there, but by default, the manufacturer (Intel and AMD) restricts the CPU’s performance to a ‘safe’ level to ensure it’s reliable for a longer time. You can choose to make your CPU work faster by changing a few settings, but there are risks – see below.
Depending on your chipset, for example having a Devil Canyon versus Ivy Bridge chipset, they will have different ways of overclocking. Therefore, if you’re looking to achieve the highest possible overclock on a specific chipset, it would be best if you followed a dedicated guide for your chipset and processor.
You’ll only be able to overclock a processor if it’s ‘unlocked’. For example, Intel has a ‘non-K’ Intel Core i7 which has a locked clock speed, preventing you from overlocking it and a unlocked-K version of its Intel Core i7, allowing you to overclock the processor.
In order to make this guide relevant for all readers, we will not concentrate on a specific chipset, but rather look at the tools and auto overclocking methods available to you. If you’re looking to fine-tune and get the maximum performance out of your processor, you’ll need to fully understand the process of overclocking and also sacrifice several weeks to overclocking, as it’s a lengthy process through trial and error.
Achieving the best overclock is no simple task and often requires a good ‘silicone lottery’. The lottery comes from various different processors having different voltage requirements to reach a certain clock rate. For example, looking at the same model Intel Core i7 3770K processor, on CPU will need 1.35 Volts for a 4.5Ghz overclock, whilst another will do 1.15 Volts for the same clock speed.
Due to the complications you might run into with overclocking a laptop, we’ve chosen to stick to desktop computers. If you’re looking to overclock a laptop you have to be extremely cautious, given that their heat dissipation is limited.
Dangers of overclocking a CPU

Before jumping into doing this, there are some risks to consider. For starters, overclocking will almost certainly void any warranty on your machine – although some are built with overclocking in mind. You may also damage your CPU or even other components by overclocking. In this guide we’ll try to make it as fail-safe as possible, whereby you shouldn’t ever run into problems nor run the risk of damaging any components.
However, if you are going to overclock your processor, you should be aware that you can damage your components by ramping up your BCLK too high, whereby the BCLK determines your motherboard’s overclock. Without getting too technical, a BCLK overclock boosts the performance of your whole motherboard, meaning anything directly connected to your motherboard will be overclocked. Yes that also includes your wireless card!
BCLK overclocking is therefore a little dangerous, but if done properly, you’ll be able to achieve fantastic results. We would suggest only doing a BCLK overclock, if you know the ins and outs of your motherboard chipset and processor.
Multiplier overclocking can also be dangerous, but is often a lot easier to understand. In order to achieve a faster processor speed, you need to increase its multiplier. In order for your processor to cope with the faster speed, you need to pump more power (volts) to it – this is known as increasing the Vcore. When you increase the Vcore, your CPU temperatures also increase as there are more volts going in and out of your processor at a ridiculously fast speed. Imagine it as a motor, the quicker the motor spins, the hotter it gets. More VCore means more cycles within your CPU and thus more heat.
Before you start
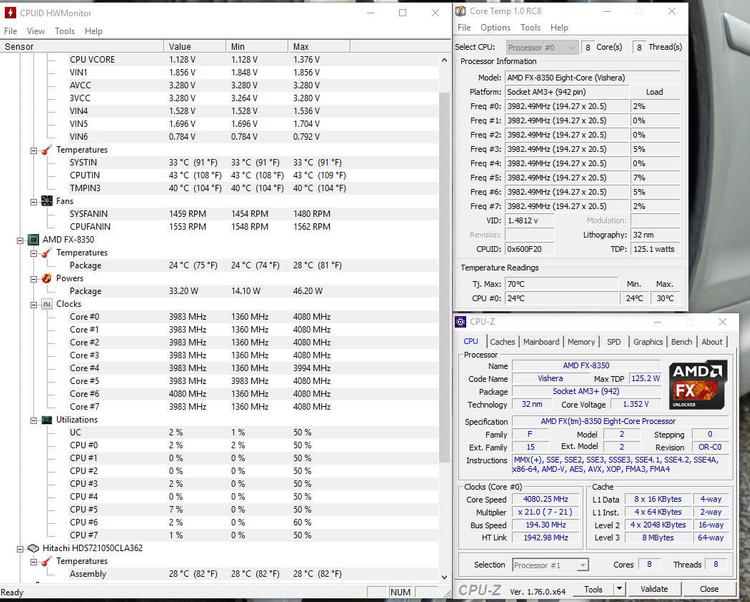
Since overclocking involves pushing your CPU beyond its factory settings, you should monitor it.
A processors maximum temperature, also known as the TJ Max is arguably the most important figure to track when overclocking, as every processor has a thermal threshold. If you exceed that temperature, your PC will have a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD); if this happens regularly you could face data loss and more importantly hardware damage with your CPU frying. If you’re going to be going above and beyond with your overclocking, we would suggest buying an after-market cooler; something like the Cooler Master Hyper 212 Evo or Arctic Freezer 7 Pro are popular choices for low-moderate overclocks. If you’re serious about overclocking, a Noctua NH-D15 or a Corsair H115i liquid cooler is what you’ll need to adequately cool your processor.
In order to be safe and always be in the know about your processor’s temperature, we suggest you download Core Temp, Real Temp or HW Monitor. This will inform you of the core temperatures of your processor and also inform you of the maximum temperature your processor can handle before it shuts off.
To test an overclock, a lot of users trust the results of Prime95, Aida64 and Cinebench, these programs put a max load on your processor and stress your processor. If it fails, you often have an un-stable overclock, whereby adjusting the Vcore is needed. We would only suggest using these programs if you’re going for a non-factory overclock. In this article we will only be covering overclocks that should be fully stable at the click of a few buttons, meaning a stress test will often not be needed as your components should be capable of coping with the low overclock you will set out to achieve.
We would also recommend downloading CPU Z, as it will display a real time measurement of each processor core’s internal frequency, your memory frequency and even your motherboard’s details.
See also: Guide to BSOD codes.
Which processors can be overclocked?

As a general rule of thumb, the higher-end processors are approved for overclocking. Not every CPU can be overclocked so you’ll need to have one which is unlocked in order to manipulate the base clock rate or multiplier.
If you’re not sure then Intel has detailed specs here or you can simply attempt to overclock and you’ll soon find out. AMD’s FX range of processors come unlocked and generally most modern AMD chips can be overclocked.
Using software to overclock a CPU
Overclocking an Intel processor
If you’re trying to overclock an Intel processor you can download the Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel XTU) software. It provides access to the settings you need to overclock such as power, voltage, core, and memory.
The software is easy to use and often safe for all types of overclockers. Again, remember that you should be constantly monitoring your CPU temperatures and maybe running a stress test like Prime95 for a few hours to ensure stability.
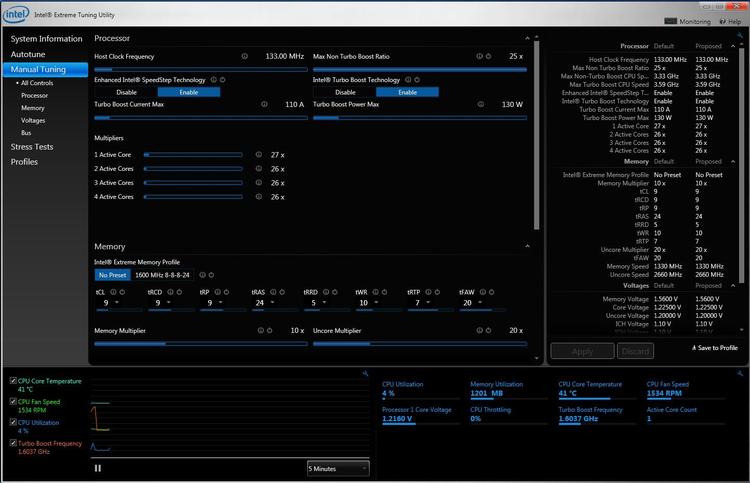
Image credits: Guru3D
Overclocking an AMD processor
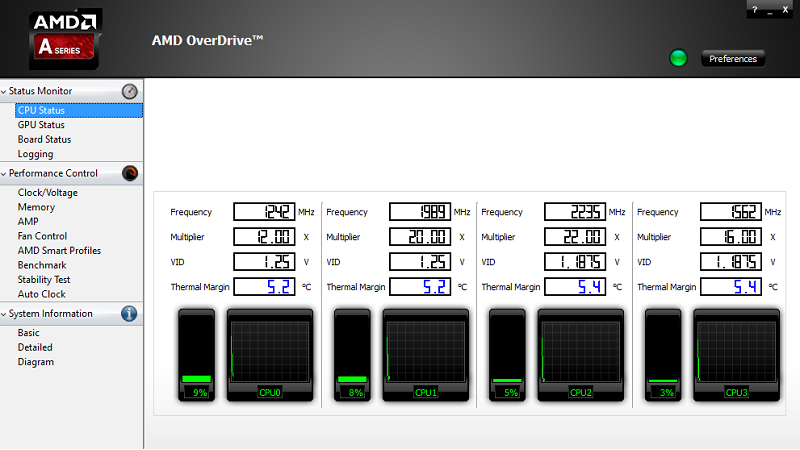
On AMD you’ll need to download OverDrive which is effectively the same thing as Intel XTU. It includes automatic tuning if you’re unsure of what you’re doing, control over your fans, monitoring and also stability tests. It’s a decent package which makes overclocking more accessible and doesn’t require multiple reboots as the changes are done in real-time.
Again, just like on Intel, you should ensure you’ve got the right monitoring tools set in place, so that you can ensure you’re not frying anything.
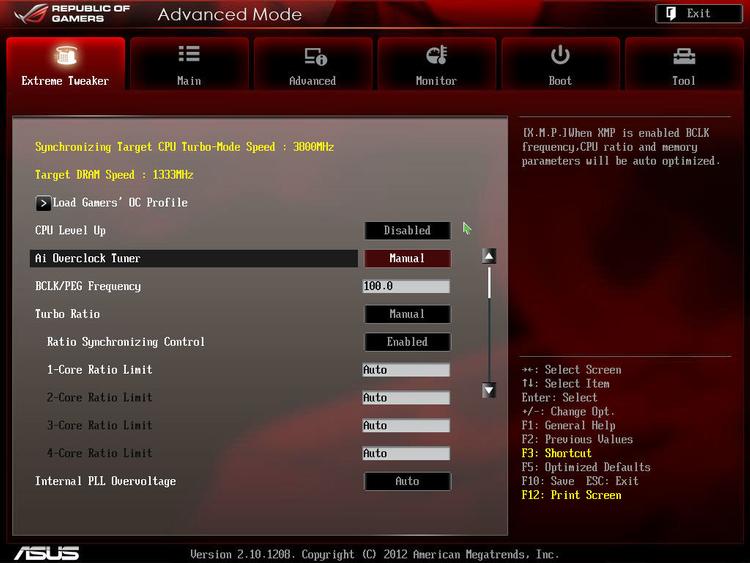
Using the BIOS to overclocking a CPU
Most overclockers, especially the experienced ones will tell you to overclock through the BIOS. This is often recommended as you won’t have any software conflicts and more so, have total control over all the settings your motherboard and processor can offer.
You can often enter the BIOS by pressing the Delete (DEL) key on your keyboard, as the PC boots up. If you’re unsure on how to access the BIOS, make sure to check our dedicate guide on entering the BIOS.
Depending on your motherboard, there should be a one-click option to overclock. For example, on mid-range and high-end Asus motherboards you should have the option to enable Ai Overclock Tuner, which will automatically provide you with a low-moderate overclock.
If you understand the BIOS and feel confident with what you’re doing, you can achieve your maximum overclock through the BIOS’ settings. Do lots of reading around your motherboard and processor and then proceed. Being over-prepared is never a bad thing!